We first compute the Jacobian for the change of variables from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates.
Recall that
![]()
Hence,
![]()
The Jacobian is
![]()
Here we use the identity cos^2(theta)+sin^2(theta)=1.
The above result is another way of deriving the result dA=rdrd(theta).
Now we compute compute the Jacobian for the change of variables from Cartesian coordinates to spherical coordinates.
Recall that
![]()
The Jacobian is given by:
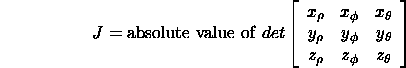
Plugging in the various derivatives, we get
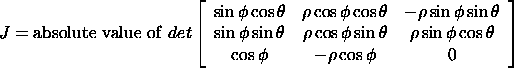
![]()
Copyright © 1996 Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University
If you have questions or comments, don't hestitate to contact us.