
The following is a list of the various namelists that can be specified in the input files. Not all of these will be used; in fact, generally very few of these will, since the program picks reasonable defaults. This list is a modification/expansion of one originally put together by Cesare Franchini. Although most of the variables and defaults should be correct, some of the more obscure parameters may not be correct; however, those will (probably) never need to be changed.
The important namelists, i.e., the ones that are used often, are &input, &allatoms, &atom, &comp, &conv, &exco, &geo, &kpt, &mix, &out, &relax. Although the list seems long, only some of the parameters are likely to be used; some of the most commonly used ones are highlighted. Although the order of the runtime namelists is unimportant (those that can be put after the structural input on the file inp or in the file para), for the structural properties, the order is important; these namelists (see Main input file: inp.) are given in italics.
A number of parameters (mainly in &conv and &mix) can be changed during the run by writing the new values to the file conv which is reread every iteration; see below.
Defaults, where applicible, are given.
- dx
- log. mesh parameter (default: 0.028)
- jri
- number of radial mesh points in muffin tins (default: 361)
- lmax
- max. l to include for charge/potential (default: 8)
- lmax_wf
- max. l to include for wave functions (default: 8)
- lnonsph
for nonspherical contributions to matrix elements (default: 4)
- rmt
- muffin-tin radius
- non_rel¶
if true, then non-relativistic calculation (default: false)
- econfig¶
electronic config: program will pick a reasonable configuration; core/valence states separated by ‘|’; scalar core states have a ‘s’ appended
Examples:
B: econfig='1s2 | 2s2 2p2' B 1s-corehole: econfig='1s1 | 2s2 2p2' Co: econfig = '[Ar] | 3d7 4s2' Co, scalar 3p: econfig = '[Ne] 3s2 3p6s | 3d7 4s2'To specify (core) occupations of relativistic levels, give j value:
econfig='1s2 2s2 2p(1/2)1 2p(3/2)4 | 3s2 3p2'By default core holes are put in the highest j level.
- element¶
- dx¶
log. mesh parameter (default: 0.028)
- id¶
atom identifier used in atomic positions
- jri¶
Number of radial mesh points in muffin tins (default: 361).
- lmax¶
max. l to include for charge/potential (default: 8)
- lmax_wf¶
max. l to include for wave functions (default: 8)
- lnonsph¶
for nonspherical contributions to matrix elements (default: 4)
- majority_spin_core¶
majority_spin_core ={0|1|2}; for magnetic systems with core hole, core moment parallel to spin {1|2} or no net core moment (0) (default: 1}
- rmt¶
muffin-tin radius (default: from internal table)
- z¶
atomic number (better to use element ) (default: same as id)
- ldau_l¶
LDA+U: l of states
- ldau_u¶
LDA+U: U (eV) (default: 0)
- ldau_j¶
LDA+U: J (eV); only U-J important (default: 0)
- ldau_alpha¶
LDA+U:
(FLL), 0 (AMF), -1 interpolate (default: 1)
contains information about band structure plots; this namelist is in the file bskpts and is only read when bsplot=t in &out
- nkpts¶
total number of k-points to plot
- cc #2¶
whether k-points are in scaled Cartesian (or lattice) units (default: false, corresponding to lattice units))
The endpoints of the segments are given in bskpts after this namelist, as:
0 0 0 0 ! Gamma 1 1 0 0The first number tells whether a segment ends (=1) or not. (The first is generally set =0). The k-points will be distributed as equally as possible.
- k_projected¶
do a “k-projected” bandstructure, .i.e., project the (supercell) bands onto a primitive cell. The k-points are given in terms of the cell the calculation is being done in. See following inputs also. (default: false)
- unitcell¶
the lattice vectors of the primitive cell to use for the projection, given as row vectors (same as in the input) with the same units. For example, a hexagonal
calculation would have inputs:
3/2 -1/2 0 ! a1 3/2 1/2 0 ! a2 0 0 1 ! a3 1 -3 -8/3 ! scaling factors unitcell = 1/2 -1/2 0 ! primitive a1 1/2 1/2 0 ! a2 0 0 1
- l_layer¶
logical to determine whether to get a layer projection also (useful for surfaces) (default: false)
- zlay1,zlay2¶
if l_layer=t, determines the layer to use; always given in scaled cartesian and assumes that a3 (for both cells) is along z
- k_shift¶
integer array in terms of the supercell reciprocal lattice vectors that shifts the origin outside the BZ of the supercell in order to choose a particular folded-back k-point without having to calculate the wave functions again. (default: (0,0,0))
- chg2cdn¶
read ascii charge file (not needed; set if file chg1 exists) (default: false)
- ctail1¶
use core tails in generation of initial cdn (default: true)
- lflip¶
flip magnetization options (default: false)
- strho¶
generates new charge density file; taken care of automatically (default: false)
- swsp¶
magnetize options (generally not need; see &swsp ) (default: false)
- e1s¶
min. energy range (relative to E F ) (default: 0)
- e2s¶
max. energy range (relative to E F ) (default: 0)
- kk¶
k-points kk is taken into account (if 0 all k-points are considered) (default: 0)
- nnne¶
number of bands to include if e1s=e2s=0.0 (default: 0)
- pallst¶
bands above Fermi energy taken into account (default: false)
- plpot¶
plot potential (default: false)
- slice¶
calculate density of energy range or single state (default: false)
- ctail¶
calculate core tails (default: true)
- epfloat¶
use floating energy parameters (default: true)
- frcor¶
frozen core approx (requires cdn1, cdnc, enpara) (default: false)
- gmax¶
max. G-vector (default: 12)
- gmaxxc¶
gmax for ex-corr. potential (default: 1.5*gmax)
- isec1¶
iteration to start iterative diag at (default: 9999)
- jspins¶
number of spins (default: 1)
- kmax¶
max k (default: 8/min(rmt))
- nstates¶
number of eigenvalues to be calculated
- cdist_eps¶
convergence criteria for charge density (default: 1.0e-3)
- cputimelimit¶
cpu time limit (default: unlimited)
- dforce_eps¶
convergence criteria for forces (default: 1.0e-5)
- eps_force¶
convergence criteria for full forces (force_mode=2,3) (default: 1.0e-5)
- evar_delta¶
convergence criteria for total energy (default: 1.0e-7)
- force_mode¶
- itmax¶
max. number of iterations for total run (default: itmax_scf*maxstep)
- itmax_scf¶
max. number of iterations for each atomic step (default: 50)
- itmin¶
min. number of iterations (default: 0)
&end on a line will stop reading input
Scale all atomic positions; must come directly after atomic positions (and &shift if used):
atompos(:,:)=atompos(:,:)/factor(:)
Flips the magnetic moment(s) within the MT; either give {1|-1} for all atom types:
&flip 1 -1 1 -1 /or just the atom type(s) to change:
&flip type 3 6 /
number and generators of the space group in internal coordinates (ngen>0) or Cartesian (ngen<0). See output files for examples (can cut and paste). Must come after atomic positions, but before runtime parameters; will set cal_symm=f
- epsdisp¶
limit for displacement to be converged (default: 0.00005)
- epsforce¶
limit for forces to be converged (default: 0.00005)
- l_geo¶
do geometry opimization (default: false)
- maxstep¶
max number of optimization steps (default: 1)
- thetad¶
approx. debye temperature (default: 330K)
- xa¶
limit of displacements (default: 0.25
)
- geo_restart_step¶
number of atomic steps that a new starting density is generated; for istep greater than this value, extrapolation of density used (default: 0)
- geofixcdn¶
charge renormalization above which a new starting density is generated (default: 0.05)
- angstrom¶
if .true., then the lattice constant or volume in Angstrom (all other units are in atomic units); simpler to add an “A” after the lattice constant, e.g., 4.08 A (default: false)
- cal_symm¶
if (true) calculate or if (false) read in space group symmetry info (default: true)
- cartesian¶
if false specification of atomic positions in lattice units, otherwise if true in scaled cartesian coordinates (default: false)
- cc¶
same as cartesian
- checkinp¶
program reads/checks input and stops; easier to use -c or –check on the command line (default: false)
- inistop¶
program stops after generating density, etc.; use -s or –setup on the command line (default: false)
- op¶
- tolerance¶
- div1¶
division along
reciprocal lattice vector (default: false)
- div2¶
division along
reciprocal lattice vector (default: div1)
- div3¶
division along
reciprocal lattice vector (default: div1)
Default k-point mesh: div1 = nint( (1024 / number of atoms)^(1/3) ). For film calculation, div3 = 1.
- cryst_len¶
crystal size (in
) to determine divN via Born-vons Karman boundary conditions
- kshift¶
shift mesh away from zone center if symmetry allowed (default: false)
- origin¶
explicit k-point mesh shift (if kshift=t): 0 or 1. is forced to be consistent with symmetry of Bravais lattice. Example: origin=0,0,1 (default: 1,1,1)
- tkb¶
Fermi function broadening in Htr (default: 0.001)
- fixed_moment¶
if /= 0, value of fixed spin moment (default: 0)
- q_ef_excited¶
charge to excite from below Fermi level to above (default: 0)
- b_field¶
external magnetic field; causes the up/down Fermi levels to be separated by 2*b_field (default: 0)
- kinv¶
use inversion (time-reversal) when generating k-mesh (default: true)
Input lattice in terms of lengths, angles, and lattice system. Either the overall (conventional) lattice parameter (a0 or a) or the volume of the primitive cell (vol) must be given. Appending an “A” denotes Angstrom units. If a0 or vol is given, then a is the scaling factor (scale(1)) and b and c are the b/c and c/a ratios, respectively; when a0 (vol) are omitted, then a, b, and c are the conventional lattices constants (all in the same units). Example: trigonal lattice:
&lattice bravais='hR' a=7.32A alpha=113.57818 /
The file inp_new will include the lattice vectors, scale factors, etc.
in case one wants to modify the cell. For rhombohedral (hR) lattices
when the angle 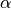 and length a are given, this will give
the lattice parameters and scaling (c/a ratio) of the equivalent
hexagonal lattice; to convert to the hexagonal lattice use:
and length a are given, this will give
the lattice parameters and scaling (c/a ratio) of the equivalent
hexagonal lattice; to convert to the hexagonal lattice use:
1/2 -1/2 0
1/2 1/2 0
0 0 3
for the lattice vectors of the 3x hexagonal cell. The three primitive cells are at (0,0,0), (1/2,1/6,1)=(0,-1/3,1), and (-1/2,-1/6,-1)=(0,1/3,2). (The stacking can be reversed if desired.) To convert the atomic positions, first output the positions in cartesian coordinates (see inp_new_pos in &out), and then switch to the hexagonal cell.
- a0¶
overall lattice parameter (add A for Angstroms). If a0 (or vol) not given, then a will be used as the overall lattice constant.
- a¶
relative length of
(scaling of lattice constant) [overall lattice constant if a0 not given] (default: 1)
- b¶
relative length of
(b/a ratio) [or b]
- c¶
relative length of
(c/a ratio) [or c]
- alpha¶
angle between
and
- beta¶
angle between
and
- gamma¶
angle between
and
- bravais¶
- vol¶
unit cell volume, use instead of a0 (add “A” for Angstroms)
- alpha #2¶
mixing parameter (default: 0.1)
- imix¶
- maxiter¶
max. depth of of history for Broyden type schemes (default: 20)
- aspin¶
spin mixing parameter (spinf=aspin/alpha) (default: 0.0)
- spinf¶
spin mixing; if imix>0 and spinf<0, straight mixing of spins spin mixing = alpha*|spinf| (default: 5)
Shift origin of all atomic positions following up until another &origin. Must come after number of atoms:
atompos(:,n)=atompos(:,n)+origin(:)
- bsplot¶
band structure calculations (default: false)
- cdinf¶
perform check continuity of cdn (default: false)
- cdnplot¶
calculate cdnplot (default: false)
- chgfile¶
write ascii charge file (chg1) (default: false)
- chgfiles¶
write ascii charge files (chg_in, chg_out) (default: false)
- dosform¶
- dosplot¶
calculate dos and generate dos plot files (default: false)
- ef0¶
fermi energy (for plotting) (default: 0)
- emax0¶
max of plot in eV
- emin0¶
min of plot in eV
- eonly¶
calculate only eigenvalues (no l-like charge) (default: false)
- eshift¶
fermi energy shift (for plotting) (default: 0)
- form66¶
formatted eigenvector file (eig) (default: false)
- geo_all¶
write geo_N.xsf file for each atomic step (default: false)
- jems¶
write structure files for JEMS (default: false)
- kptfile¶
write kpts file (default: false)
- lpr¶
if > 0, more output (e.g., eigenvectors) (default: 0)
- inp_new_pos¶
determines the output form of the positions in inp_new. Default is same form as input; c or C for scaled Cartesian, and l, L, d, or D for lattice (direct) cooridinates. (Useful for changing format).
- l_diffraction¶
calculates the surface diffraction pattern and generates an xmgrace plot. Assumes that a_3 is the perpendicular direction. (default: false)
- l_reps_only¶
controls output to inp_new when only representatives given; .f. will cause all atoms to be written (default: true)
- nmesh¶
number of mesh point for DOS
- pdist¶
potential distance is calculated (default: false)
- pot_plot¶
plot planar-averaged Coulomb potential for films/surfaces. For bulk supercells, a3 must be perpendicular to :math”a_1, a_2) (default: false)
- potfile¶
write ascii potential file (potential) (default: false)
- symfile¶
write sym ops to file sym (sym.out) (default: false)
- tkb0¶
Fermi broadening for plotting in Htr (default: 0.005)
- units¶
e=eV, r=Ry, and h=Htr (default: e)
- valcdnfile¶
write unformatted valence density (valcdn) (default: false)
- vchk¶
perform potential check (default: false)
- fermi_surface¶
plot Fermi surfaces (see ef_fs, fs_range) (default: false)
- ef_fs¶
For Fermi surface plots,
(in hartrees) to use. (default: use calculated
)
- fs_range¶
include all bands within +/- fs_range (eV) (default: 0.5)
- stm_plot¶
determines and generates plots for constant current stm. For constant height plots, set stm_height > 0. Can be run using itmax=0. Will generate a file stm.dat that depends on the selected bias (=0 corresponds to Fermi level), and requires that the eig file(s) be available. the Fermi level used is (in this order):
- ef0 from &out,
calculated during the run, or
- will calculate it again.
The plot area given in the &plot and &plotarea namelists will be used if defined; otherwise, will define a rectangular area that includes a full unit cell, possibly cut oddly. To do line profiles, set either n1 or n2 =1 in &plot (default: false)
- stm_bias¶
- stm_surface¶
surface to plot: {‘top’|’bottom’} = outward normal {increasing|decreasing} z (default: top)
- stm_contour¶
density to follow; if <0, then will pick a reasonable value (default: -1)
- stm_spin¶
- stm_angle¶
angle (in degrees) between polarization directions of the tip and surface (default: 0)
- stm_tip_polarization¶
assumed tip polarization: varies between 0 (unpolarized) and 1 (fully) (default: 1)
- stm_height¶
for constant height (as opposed to constant current), set to height in Angstoms above the surface; must be at least 1 A (default: 0)
- vasp_poscar¶
generates an input POSCAR file suitable for use in VASP (default: false)
- cc #3¶
scaled Cartesian coordinates for plot-box (default: false)
- cart¶
full Cartesian coordinates (in a.u.) for plot-box (default: false)
- cdnselect¶
select what to plot: If slice=t (see &cdnslice ), the density in the file cdn_slice will be used; must be:
‘c’ (charge),‘s’ (spin),‘cs’ (charge and spin),‘c1’ (spin up), ‘c2’ (spin down), or‘c1c2’ (both spins)(default: c, cs)
- dim¶
dimensiononality of the box (2D or 3D) (default: 3)
- n1¶
points along first direction (default: 0)
- n2¶
points along second direction (default: n1)
- n3¶
points along third direction
- nplot¶
number of plots (i.e., # of &plotarea namelists) (default: 1)
- score¶
remove core charge (default: false)
Plot charge density (2D or 3D) in file cdn.dat &plot must appear before &plotarea. Give origin and then vectors for axes.
Example 2D:
&plot dim=2 cc=f n1=50 n2=50 nplot=1 cdnselect='c' score=f / &plotarea 0.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 /Example 3D:
&plot dim=3 cart=t n1=50 n2=50 n3=40 nplot=1 cdnselect='c' score=t / &plotarea 0.0 0.0 0.6 8.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 8.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 8.0 /
For geometry optimization: ignored unless l_geo=t in &geo. A triplet of {0|1}s specifying whether each (x,y,z) component of the atomic position is allowed to relax (1) or not (0).
Two different formats are allowed:
Old style: each atom type must be specified in order: example: &relax 001 111 000 / specifies relaxation in z for 1st, all directions for 2nd, and no relaxations for 3rd atom type.
New (and preferred) style: only list the atom types that need to be changed using atom_type = triplet or n1:n2 = triplet where n1:n2 represent a range of atom types; if n2 is omitted, then defaults to ntype. Default can be changed (from 111) by using the keyword default=.
Example: &relax 3=000 1=001 /specifies relaxation in z for 1st, no relaxation for 3rd, all other atom types fully relaxed.Example: &relax default=001 4=111 2=000 9:=111 /Default to relax z only, fully relax 4th, freeze 2nd type, and fully relax atom types 9 to ntype(default=111)
Shift origin of all atomic positions. Must come directly after atomic positions:
atompos(:,1:nat)=atompos(:,1:nat)+shift(:)
Starting spin moment for the spin-polarized case given in terms of: atom kinds (identifiers) as used in positions:
Example: &swsp kind 26=2.0 28=0.5 / (“kind” optional)Using atom types: &swsp type 3=2.0 2=0.5 /List by atom type: &swsp 0.0 0.5 2.0 0.0 /Can also give orbital occupations (density matrix) for given atom kinds (not types):
&swsp 26=[ up: d_xy=1 d_z2=1 d_xz=1 d_yz=1 down: d_x2-y2=1 ] /“[” , “]”, “up:”, and “down:” are required. Orbitals are denoted by “p_x, p_y, p_z, d_xy, d_yz, d_xz, d_z2, d_x2-y2”, in obvious notation. Occupations should be between 0 and 1.
Number and operations of the space group in internal coordinates see output files and &gen for examples must come after atomic positions, but before runtime parameters.
A number of parameters can be changed during the run.
To do so, create a file conv. The existence of this file will be checked at the end of each iteration. If it exists, it will be read and the parameters changed. Each line of the file should be of the form keyword=value (one per line).
The parameters that currently can be changed are:
- cdist_eps
- cputimelimit
- dforce_eps
- eps_force
- evar_delta
- force_mode
- itmax
- itmax_scf
- itmin
- maxstep
- tkb
- alpha
- imix
- spinf