|
Functional Group |
Functions |
Diagram |
More examples |

|
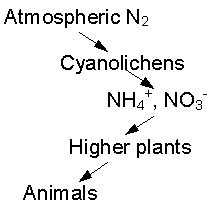
Cyanolichens fix nitrogen, converting biologically
inactive nitrogen gas into forms usable by higher plants. Many
conifer forests in the PNW are nitrogen limited. |
|
Pseudocyphellaria rainierensis
Lobaria oregana
Nephroma occultum |

|
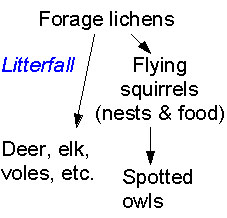
The dangling hair-like forage lichens are eaten
by many animals, including deer, elk, flying squirrels, and other
animals. These lichens are also commonly used as nest materials |
|
Alectoria,
Bryoria,
Mule deer eating Bryoria,
Usnea longissima |

|
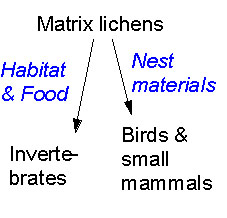
Matrix lichens are relatively fast invaders of
new branches. They provide food and shelter for arthropods, molluscs,
and mammals. Matrix lichens also provide nesting material for
birds. |
|
Hummingbird nest camouflaged
with Parmelia
Bushtit nest made of spider webs
and the lichen Physcia
Hypogymnia |

|
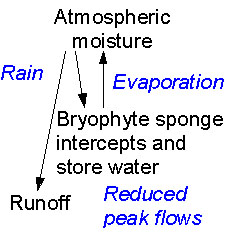
Bryophytes are relatively inedible by most animals,
but can act as hydrologic buffers by absorbing and evaporating
precipitation. Bryophyte mats are also involved in nutrient accumulation
and release. |
|
Antitrichia curtipendula
Kindbergia oregana,
Neckera douglasii,
mossy bigleaf maple |
|
Functional Group |
References |
|
Cyanolichens |
Nitrogen fixation: Antoine 2001,
Brown & Dalton 2002,
Denison 1973, Denison
1979, Holub & Lajtha
2004, Pike et al. 1972,
Pike 1971, Pike
1978, |
|
Forage lichens |
Deer and elk: Cowan 1945, Negi 1996, Stevenson
1978, Robbins 1987, Rochelle 1980, Stevenson
& Rochelle 1984; Ward 1999
(including good literature review); Ward
& Marcum 2005; Mountain caribou: Edwards
et al. 1960, Rominger
et al. 1994; Rominger
et al. 1996; Rominger
& Oldemeyer 1989, Servheen
& Lyon 1989; Flying squirrels: Hayward
& Rosentreter 1994, Lehmkuhl
et al. 2004, Maser et al.,
1985, 1986; Rosentreter
& Eslick 1993, Rosentreter
et al. 1997, Zabel &
Waters 1997; voles: Esseen
& Renhorn 1998a, Hayward
1994, Hayward & Rosentreter
1994. |
|
Matrix lichens |
See "invertebrate uses" below. |
|
Bryophytes |
See "hydrology", "nutrient cycling" and "invertebrate
uses" below. For more information on functional roles, ecology, and uses by
animals and humans, see Janice Glime's online book on bryophyte ecology. Commercial moss harvesting, see Peck
1997; Peck & McCune
1998; Peck & Muir 2001a,
2001b; Muir
2004. See summary and download pdf
of Muir's 2004 report on commercial moss harvest in the U.S.
See also Jeri
Peck's website, for information on commercial moss harvest in the
Pacific Northwest. Information is also available from
Sam Staddon on commercial moss harvesting in Scotland. See a
website
with a summary and her report. |
|
Various |
Hydrology: Pypker 2004; Pypker et al. 2005, 2006a, 2006b.
Invertebrate uses of epiphytes: Andre
1985, Andre 1986, Davidson
et al. 1990, Gerson 1973,
Gerson 1982, Gerson
& Seaward 1977, McCune
& Day 1994, Neitlich
1993, Stubbs 1989; Nutrient
cycling (other than nitrogen fixation): Coxson
et al. 1991, Knops et al.
1996, Nadkarni 1981,
Nadkarni 1984, Pike
1971, Pike 1978. |









