PH 212
Rigid rotational motion
- Center of mass
- Rotational energy
- Moment of inertia
- Torque
-
Rotational dynamics
- Fixed axis
- Static equilibrium
- Rolling
- Vector description
- Angular momentum conservation

© 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc
The broom balances at its center of mass. If you saw the broom through its center of mass and weigh the two parts, which part will weigh more?
An unconstrained object rotates about its center of mass.
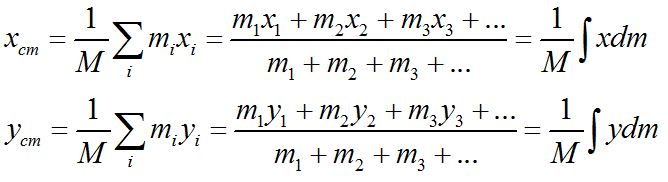

A rotating object has kinetic energy due to the motion of its particles.

© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc

Note that the radius for each mass element is the distance of the mass element from the axis of rotation.
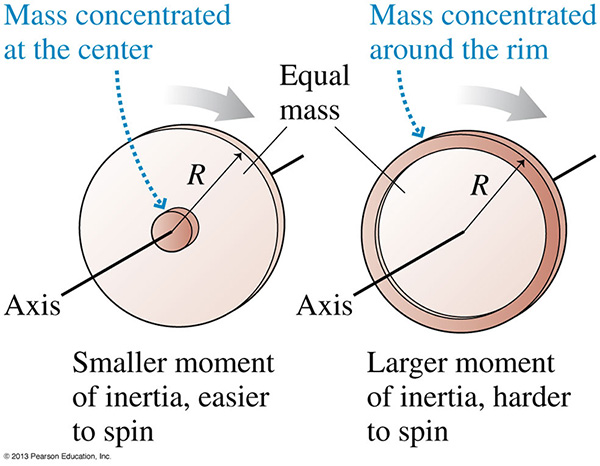
The moment of inertia, I, is a measure of the mass distribution of a rotating object. Its definition depends on the axis of rotation. A larger moment of inertia means an object needs more torque to produce an angular acceleration.

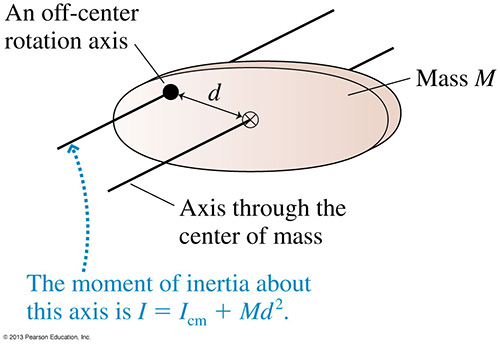
Parallel axis theorem
If an object is made to rotate about an axis that does not go through the center of mass, the moment of inertia can be found using the parallel axis theorem.
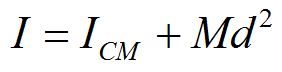
Practice problem

Consider a cylinder of radius r and mass m, with a string wound around it, starting from rest.
How what is the velocity of the center of mass of the cylinder when it has fallen a distance h?
Image source