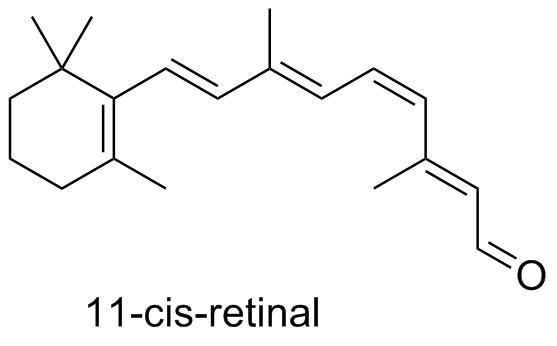
 The aldehyde functional group reacts with free amines in the side chains of lysine residues in the rhodopsin protein in your macular cells. This is the same condensation reaction we talked about in Chapter 17. When this derivatized protein captures a photon, it undergoes E/Z isomerization. That causes a major conformational change in the protein that initiates a sequence resulting in an electrical signal in your brain: and you see the light!
The aldehyde functional group reacts with free amines in the side chains of lysine residues in the rhodopsin protein in your macular cells. This is the same condensation reaction we talked about in Chapter 17. When this derivatized protein captures a photon, it undergoes E/Z isomerization. That causes a major conformational change in the protein that initiates a sequence resulting in an electrical signal in your brain: and you see the light!
Show all the lysine residues
Zoom in
Display protein backbone trace
Display isomerizing C=C bonds