 |
PHILIP R. WATSON, PROFESSOR
B.A. Oxford University, 1974
Ph.D. University of British Columbia, 1979
Department of Chemistry, Oregon State University,
Corvallis, Oregon 97330-4003, USA
Phone : (541)-737-6740 Fax : (541)-737-2062
E-mail : watsonp@chem.orst.edu |
NIST Surface
Structure Database (SSD)
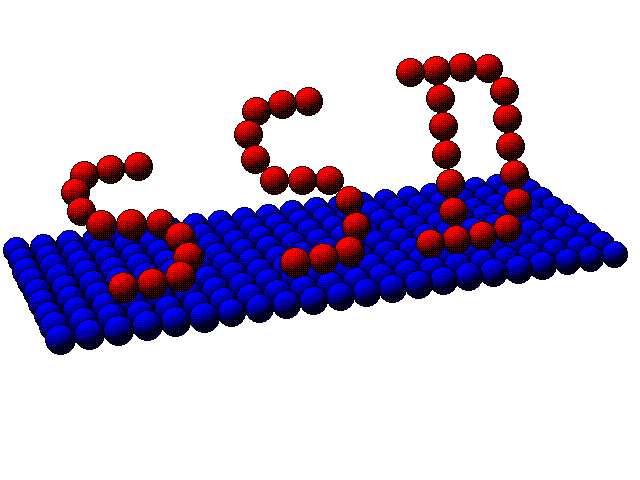
The Surface Structure Database (SSD) is a collaborative project with Dr. Michel Van Hove, Lawrence Berkeley National
Laboratory and Prof. Dr.
Klaus Hermann, Fritz-Haber Institute, Berlin under the auspices of the National
Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). SSD is the only complete critical
compilation of reliable crystallographic information now available on surfaces and
interfaces.
What does SSD
contain?
Easy searching
Data screens
Graphics
SSD version 3.0
Hardware
requirements
How to obtain
SSD
How
to contribute a structure to SSD
Publications
about SSD
What
does SSD contain?
SSD brings instant access to detailed text and graphical
displays of over 1100 experimentallydetermined atomic-scale structural analyses.
Using the powerful, yet easy-to-use capabilities of SSD, scientists in physics, chemistry,
and materials science can quickly and easily find the answer to such questions as :
what adatom structures on compound semiconductors have been solved?
what are the coordinates of the atoms at the CoSi2/Si
interface?
how many studies on Ag surfaces have appeared since 1980?
do C-C bond lengths vary in adsorbed hydrocarbons?
how do different surfaces of Si reconstruct?
has the Al/GaAs (110) system been studied with LEED?
Easy
searching
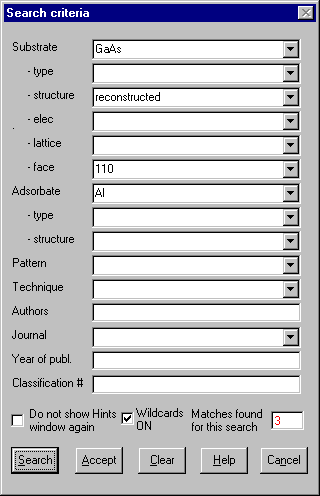
Searching for needed information has been made as painless as possible
and context-sensitive on-line help is available at all times. Searches involve simply
filling in the blanks with each criterion of interest and clicking the mouse - no
arcane and repetitive search procedures!
If you are not sure of the spelling or would like some suggestions,
simply double-click the mouse to see a list of possibilities for that criterion. You can
search for specific items (e.g. Si substrate, (111) crystal face, Al adsorbate), or for
classes of materials or structures (e.g. metallic substrates, molecular adsorbates,
reconstructions).
Data screens
The database provides a wealth of information for each structure using
5 data screens:
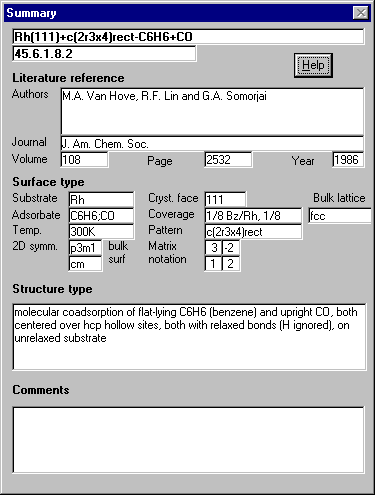
Summary - full reference and brief summary of the suface structure
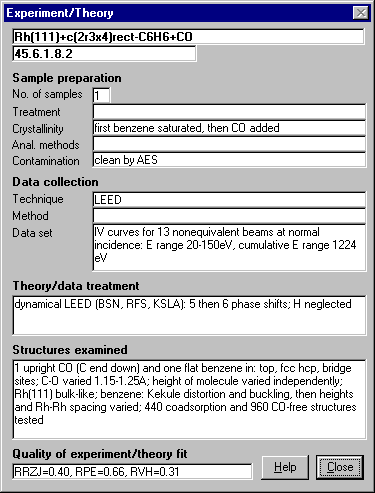
Experiment/Theory - details of sample preparation, experimental
technique, dataset and theoretical analysis
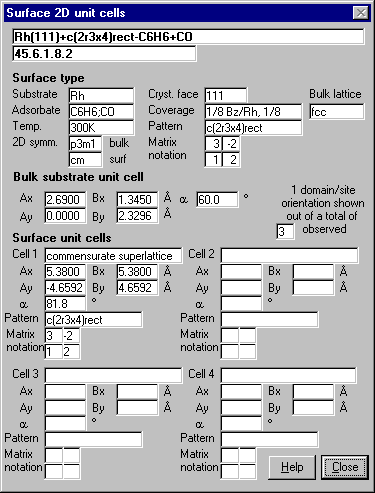
Surface 2D Unit Cells - complete description of the bulk and surface
unit cell(s)
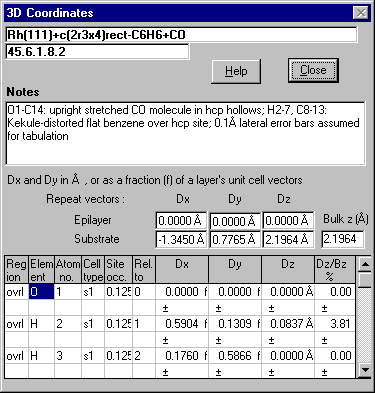
3D Coordinates - scrollable list of coordinates, with error bars, for
surface or interface atoms
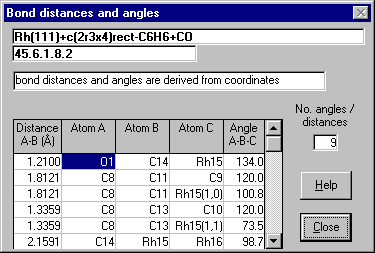
Bond Distances and Angles - scrollable list of important bond lengths
and angles
Any or all of this information can be printed out in a convenient form
suitable for reports.
Graphics
However, SSD is more than a critical compilation of data. This database
contains integrated 3D color graphics that allow you to visually inspect all surface
structures.
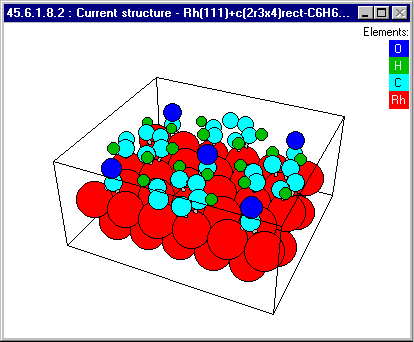
You have complete control over the appearance of the 3D display :
rotation, magnification and choice of perspective
display of atoms as circles, disks, shaded spheres, etc.
color or gray-scale publicaton-quality PostScript output
full-color or red/blue stereo modes
choice of colors for atoms, bonds and background
The visualization capabilities of SSD extend beyond display to
interactive analysis of structural relationships :
storage and comparison of related structures
interatomic distances and bond angles
number and distance of neighbors and much more.
SSD version 3.0
Version 3.0 of SSD is scheduled to appear in summer 1999. It will offer the following
main changes from version 2.0 :
- The software has been completely rewritten to run under Windows 95/98/NT. It utilizes
simultaneous windows and new menus to present data more comprehensively and rapidly.
- The structural data will be expanded to cover structures published since about mid-1995.
Hardware
requirements
Intel 80486 or Pentium processor
16 MB or more of memory
VGA graphics with at least 256 colors and color monitor with 800x600 pixels or higher
resolution
10 MB of free hard disk space (15 MB for installation)
Microsoft Windows-compatible mouse; printer (optional; required for print output of
listings, PostScript type for printing graphics).
The SSD software and data are marketed by the NIST Standard Reference Data Program as
Database 42. Further information, including ordering instructions, can be obtained at the NIST SSD web site
How
to contribute a structure to SSD
Information on how to contribute a structure to SSD is available at http://electron.lbl.gov.
Publications about
SSD
ELECTRONIC DATABASE: Surface Structure Database (SSD), P.R. Watson, M.A. Van
Hove and K. Hermann, NIST Surface Structure Database Ver. 1.0, NIST Standard Reference
Data Program, Gaithersburg, MD, USA (1993).
BOOK: Atlas of Surface Structures, Based on the NIST Surface Structure Database (SSD),
P.R. Watson, M.A. Van Hove and K. Hermann, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, Monograph No. 5, in 2
Vols. (1A and 1B) (1994).
ELECTRONIC DATABASE: Surface Structure Database (SSD) Version 2, P.R. Watson, M.A.
Van Hove and K. Hermann, NIST Surface Structure Database Ver. 2.0, NIST Standard Reference
Data Program, Gaithersburg, MD, USA (1996).
PAPER The Surface Structure Database: SSD, M.A. Van Hove, K. Hermann
and P.R. Watson, in The Structure of Surfaces V, Proc. ICSOS-V, Eds. P.
Soukiassian, G. Le Lay and M.A. Van Hove, Surf. Rev. Lett. 4, 1071-75 (1997).
Top of page
http://www.chem.orst.edu/PersonalHomePages/Research/SSD.htm
Last Updated by Philip R. Watson on Monday, September 09, 2002








