Exam 1 CH 130 Name ________________________
April, 2001 Circle your name if you want to pick up graded exam personally
There are 6 pages and 28 questions on this exam. Be sure you have them all.
Write your answers to the multiple choice questions in the numbered boxes on the last page of this exam. Each of the 24 multiple choice problems is worth 3 points.
1. Which group is the best description of the properties of alkanes?
A. Flammable, reactive, water soluble
B. Non-flammable, non-polar, water soluble
C. Flammable, non-reactive, insoluble in water
D. Non-flammable, polar, reactive
E. High melting, colored, reactive
2. Two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but with the atoms connected differently are referred to as
A. normal alkanes
B. isomers
C. conformations
D. branched alkanes
E. cyclic hydrocarbons
3. Which molecule is not an isomer of the molecule C2H5-O-C2H5 ?
A. CH3-O-CH2CH2CH3
B. C4H9OH
C. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
D. CH3CH(CH3)CH2OH
E. CH3CH2COCH3
4. How many carbon atoms are there in the longest continuous chain of the molecule (CH3)2CH-(CH2)5-CH3
A. 9
B. 8
C. 7
D. 5
E. Cannot be determined without additional information
5. In the molecule 3,3-dimethylhexane, carbon number 3 is
A. primary B. secondary C. tertiary D. quaternary E. none of these
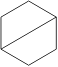
6. Which molecule is NOT an isomer of cyclohexane, :
A.
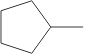
B.
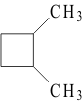
C. D. E.

7. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown:
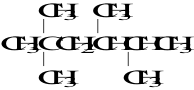
A. 2-dimethyl-4,5-dimethylhexane
B. 2,2,4,5-tetramethylhexane
C. 2,2,4-trimethyl-4-isopropylpentane
D. 2,3,4,5-tetramethylpentane
E. 5-ethyl-2,3-dimethylhexane
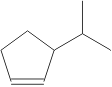
8. How many hydrogens are present in the molecule shown:
A. 6 B. 18 C. 14 D. 16 E. 12
9. Which one of the following statements is true?
A. alkane cracking and reforming are the same process
B. reforming an alkane makes long chains of carbons
C. cracking involves removing carbon-carbon double bonds with heat and pressure
D. cracking means completely breaking an hydrocarbon into its elements
E. cracking an alkane is a way to produce alkenes
10. Alkanes and alkenes are similar in all of the following properties except
A. low toxicity
B. reactivity
C. flammability
D. insolubility in water
E. solubility in non-polar solvents
11. Which one of the following molecules can have geometric isomers?
A. CH3CH=CCl2
B. (CH3)2C=CHCH3
C. (CH3)2C=C(CH2Cl)2
D. CH3CH=C(CH3)2
E. CH3CH=CHCH3
12. Which molecule is not an isomer of the molecule C2H5-O-C2H5 ?
A. CH3-O-CH2CH2CH3
B. CH3CH2COCH3
C. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
D. C4H9OH
E. CH3CH(CH3)CH2OH
13. All the following are properties of alkenes except
A. soluble in hydrogen-bonding solvents such as water
B. low boiling points
C. flammable
D. more reactive than corresponding alkanes
E. may exist as cis-trans isomers
14. Chemical reactions involving carbon-carbon double bonds are generally referred to as __________ reactions.
A. combustion B. addition C. substitution D. reduction E. oxidation
15. What monomer unit is used to produce the polymer represented as
-CH2-C(CH3)2-CH2-C(CH3)2-CH2-C(CH3)2-CH2-C(CH3)2-
A. ethylene
B. propene (or propylene)
C. 2-butene
D. 2-methylpropene (or 2-methylpropylene)
E. 1-butene
16. Which property of thiols makes them useful as additives to natural gas?
A. flammability B. solubility C. odor D. color E. disinfectant
17. Mild oxidation of R2CH-OH would produce a(an)
A. aldehyde B. alkenes C. ketone D. carboxylic acid E. no reaction
18. All the following properties of alcohols are affected by hydrogen bonding except
A. boiling point
B. solubility in water
C. ability to dissolve polar substances
D. molecular weight
E. None of the above
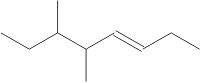
19. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown to the right:
A. 3,4-dimethyl-5-octene
B. 5,6-dimethyl-3-octene
C. 5,6-dimethyl-octane
D. 5,6-dimethyl-3-decene
E. trans-3-octene
20. Which of the following molecules would have the lowest boiling point?
A. CH3 – CH2– CH2 – OH
B. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
C. CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH3
D. CH3 – CH2 – O – CH3
E. CH3 – CH2 – CH2– O – CH3
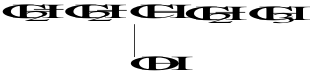
21. The molecule shown is a ______ alcohol because _________.
A. primary; it has one OH group
B. primary; the molecule is symmetric around the OH group
C. secondary; there are two carbons on either side of the carbon containing the OH group
D. secondary; the carbon bonded to the OH group is bonded to two other carbons
E. tertiary; the OH group is bonded to the number 3 carbon
22. What is the IUPAC name of the compound: CH3 – CH2 – O – CH3
A. 1,2-etherpropane B. dimethyl ether C. ethylmethyl ether D. propyl ether E. isoproyl ether
23. Why is diamond extremely hard while graphite is very soft?
A. Diamond contains far more bonds than graphite
B. The bonds in diamond are stronger than the bonds in graphite
C. The carbon-carbon bonds in diamond extend in 3 dimensions whereas in graphite they are in 2 dimensional sheets which can slide past each other
D. The carbons in diamond are hybridized sp2 whereas in graphite they are hybridized sp3
E. To deform the diamond structure one must break many bonds in all directions whereas in graphite one need only break the bonds in the sheets.
24. The following question refers to the laboratory experiment on vitamin C Suppose 4 drops of orange juice require 5 drops of DCP whereas 2 drops of standard 0.50 mg/mL vitamin-C solution require 5 drops of DCP. What is the concentration of vitamin-C in the orange juice in mg/mL?
A. 1.5 mg/mL B. 0.50 mg/mL C. 0.13 mg/mL D. 2.0 mg/mL E. 0.25 mg/mL
25. What polymer would result from polymerizing CH3-CH=CHCl? Draw enough of the polymer to be sure your answer is clear.
5 pts
26. Draw the molecule known as glycerol.
5 pts
27. Draw four structural isomers of C6H14. You may omit the hydrogens if you wish.
8 pts
28. Identify by name the functional groups in aldosterone (write each name next to its group):
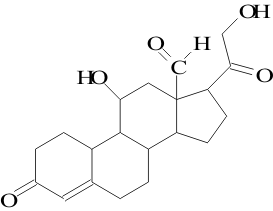
10 pts
Multiple choice answers: put the correct letter in each box
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
# correct__________×3 =
Problems 25-28 =
Total Exam Points ____________