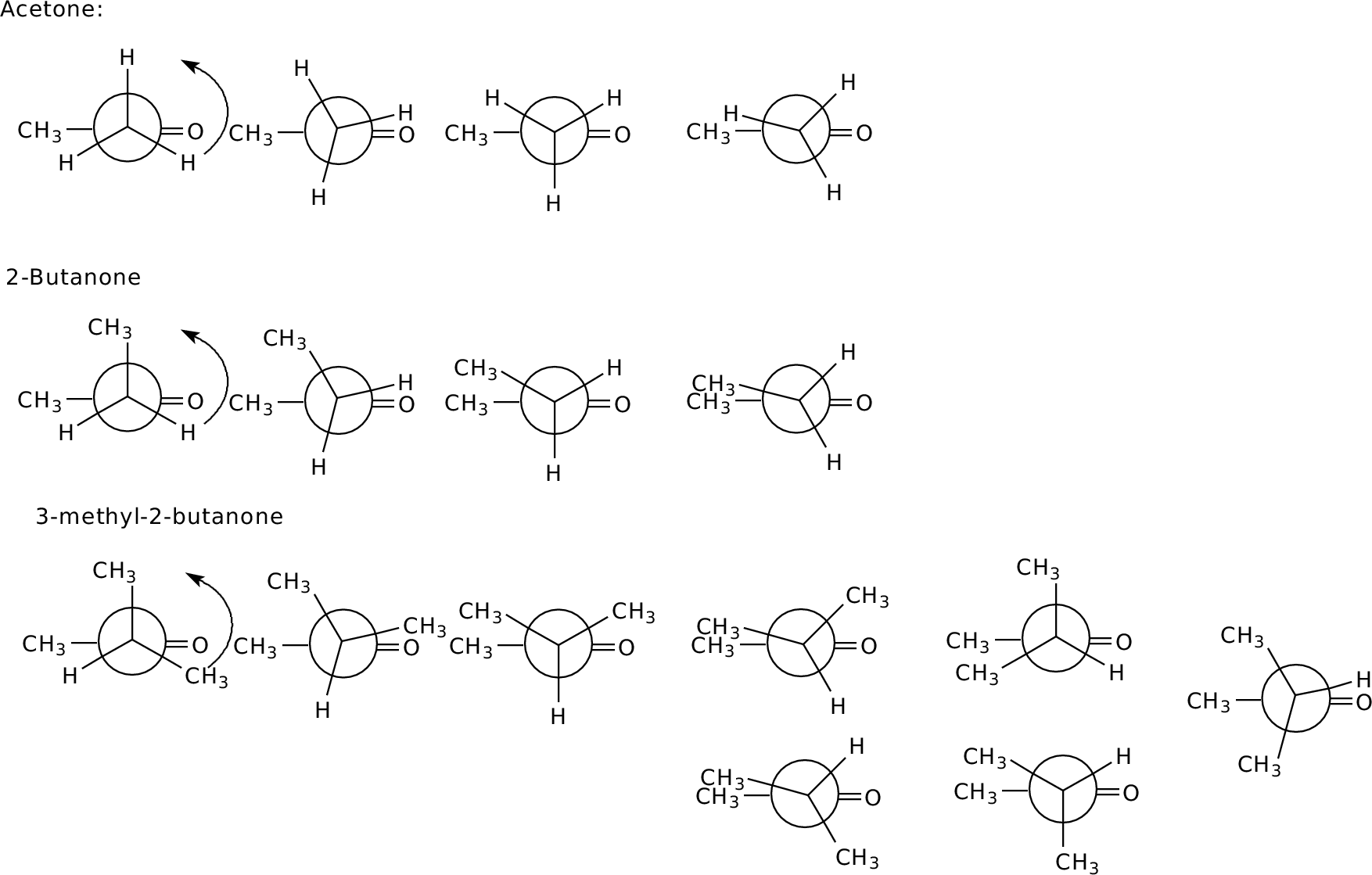
Each is symmetric; the maximum energy has a12 strain between the acetyl methyl and a substituent on C3.
2.6. 
Each is symmetric; the maximum energy has a12 strain between
the acetyl methyl and a substituent on C3.
2.8 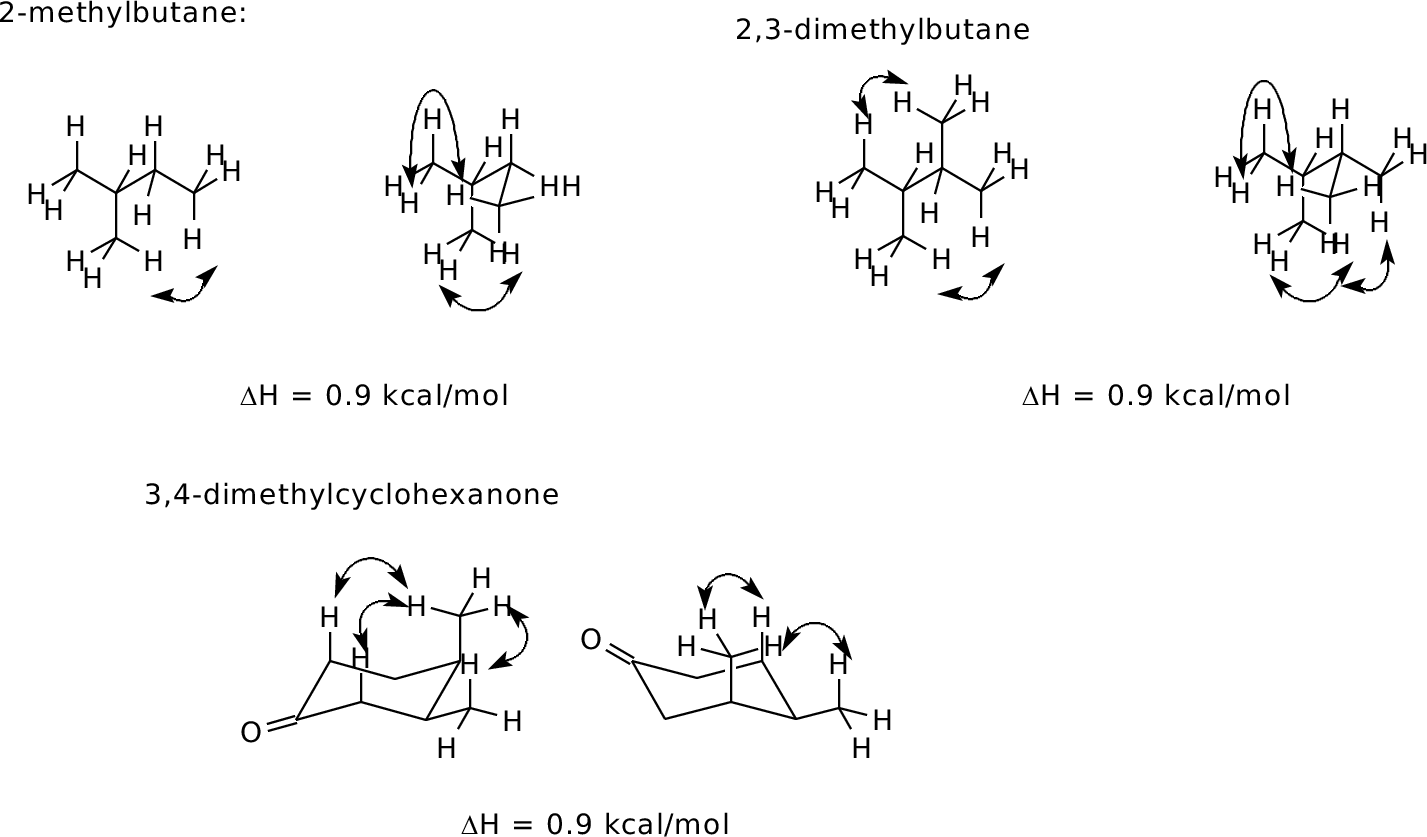
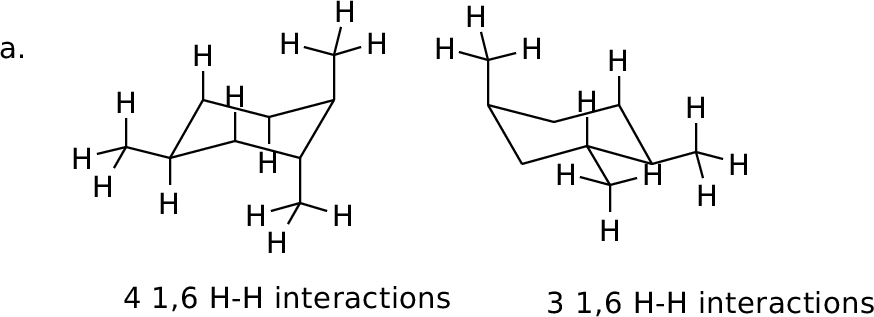
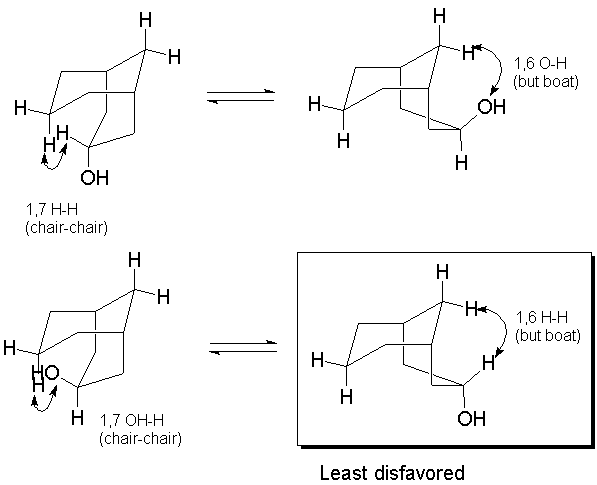
Orient in diamond lattice and count 1,6 H-H interactions in each
form.
2.9
 MM calculated difference: 0.5 kcal/mol |
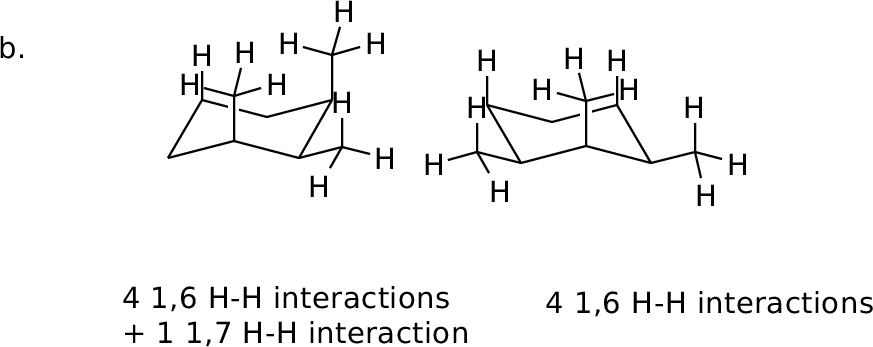 MM calculated difference: 3.5 kcal/mol |
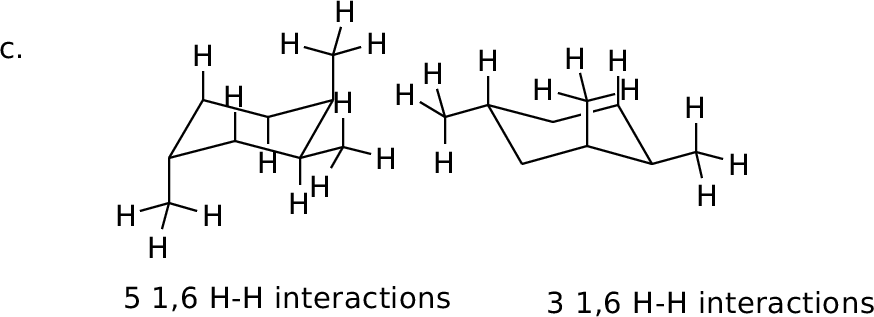 MM calculated difference: 1.5 kcal/mol |
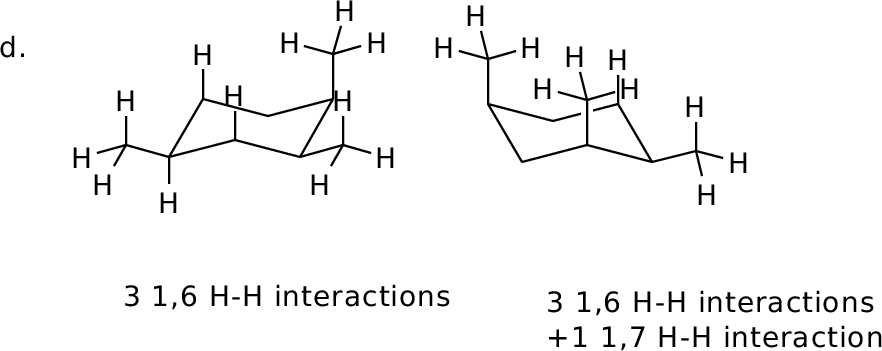 MM calculated difference: 3.5 kcal/mol |
B.1
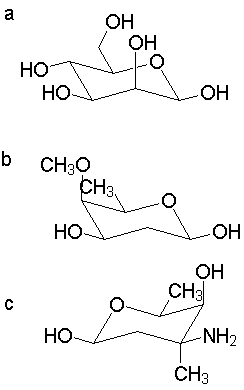
Comments:
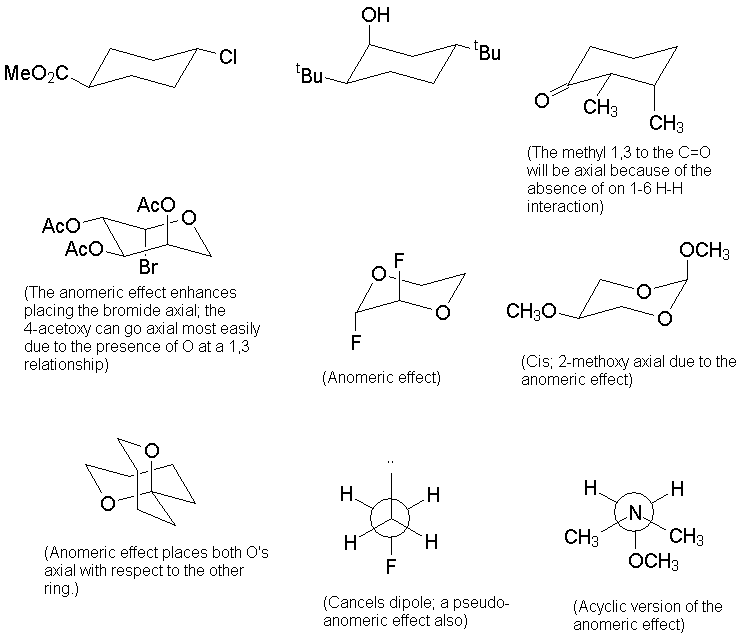
a. A simple starting point is b-D-glucopyranose, which has all substituents equatorial. Mannose is the 2-epimer of glucose; placing one group axial is better than 4.
b. Likewise, in this compound the 4-position is opposite that in glucose, and there is no 2- or 6-substitution. One axial methoxy is better than 3 others, especially where the other three are all 1,3-related.
c. Start with the mirror image of the b-pyranose ring to capture the L configuration. The axial methyl group is a problem, but the ring flip isomer is worse.
B.2.
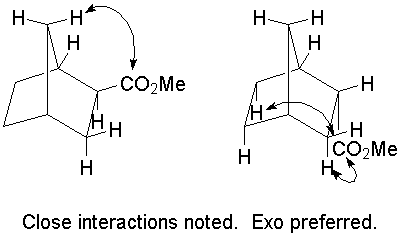
B.3 a.
b.
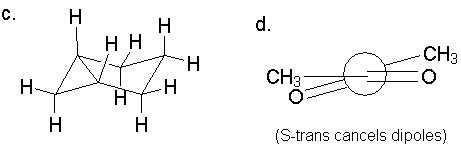
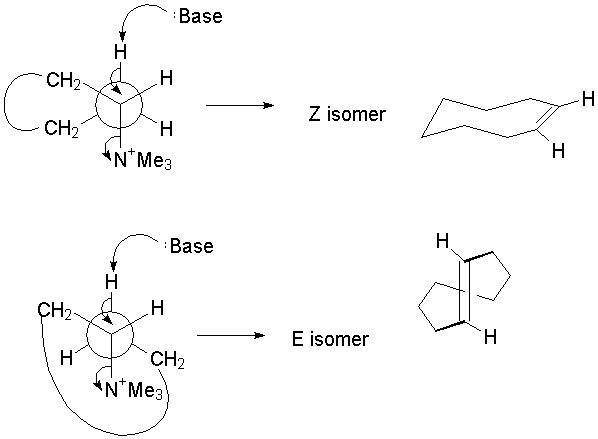
B.4. The cis comes from the "crown" form, whereas the trans comes from a distorted boat-chair. (A syn elimination is also possible that does not require as much distortion in the ring.) Note that there are syn eliminations also; one leading to each.