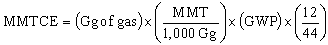








|
NATIONAL EMISSIONS

Global Warming
Potentials
.gif) Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the
greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly. Direct effects occur
when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas; indirect radiative forcing
occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a
gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, or when a gas influences the
atmospheric lifetimes of other gases. The concept of a Global
Warming Potential (GWP) has been developed to compare the ability of
each greenhouse gas to trap heat in the atmosphere relative to
another gas. Carbon dioxide was chosen as the reference gas to be
consistent with IPCC guidelines. Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the
greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly. Direct effects occur
when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas; indirect radiative forcing
occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a
gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, or when a gas influences the
atmospheric lifetimes of other gases. The concept of a Global
Warming Potential (GWP) has been developed to compare the ability of
each greenhouse gas to trap heat in the atmosphere relative to
another gas. Carbon dioxide was chosen as the reference gas to be
consistent with IPCC guidelines.
.gif) Global Warming Potentials are not provided for the
criteria pollutants CO, NOx, NMVOCs, and
SO2 because there is no agreed upon method to
estimate the contribution of gases that have only indirect effects
on radiative forcing (IPCC 1996). Global Warming Potentials are not provided for the
criteria pollutants CO, NOx, NMVOCs, and
SO2 because there is no agreed upon method to
estimate the contribution of gases that have only indirect effects
on radiative forcing (IPCC 1996).
.gif) All gases in this executive summary are presented
in units of million metric tons of carbon equivalents (MMTCE).
Carbon comprises 12/44ths of carbon
dioxide by weight. The relationship between gigagrams (Gg) of a gas
and MMTCE can be expressed as follows: All gases in this executive summary are presented
in units of million metric tons of carbon equivalents (MMTCE).
Carbon comprises 12/44ths of carbon
dioxide by weight. The relationship between gigagrams (Gg) of a gas
and MMTCE can be expressed as follows:
.gif) 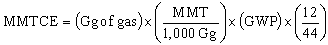
.gif) The GWP of a greenhouse gas is the ratio of global
warming, or radiative forcing – both direct and indirect – from one
unit mass of a greenhouse gas to that of one unit mass of carbon
dioxide over a period of time. While any time period can be
selected, the 100 year GWPs recommended by the IPCC and employed by
the United States for policy making and reporting purposes were used
in this report (IPCC 1996). GWP values are listed below in Table
ES-6. The GWP of a greenhouse gas is the ratio of global
warming, or radiative forcing – both direct and indirect – from one
unit mass of a greenhouse gas to that of one unit mass of carbon
dioxide over a period of time. While any time period can be
selected, the 100 year GWPs recommended by the IPCC and employed by
the United States for policy making and reporting purposes were used
in this report (IPCC 1996). GWP values are listed below in Table
ES-6.
Table ES-6: Global Warming
Potentials(100 Year Time
Horizon).gif)
| Gas |
GWP |
| Carbon
dioxide (CO2) |
1 |
| Methane
(CH4)* |
21 |
| Nitrous
oxide (N2O) |
310 |
| HFC-23 |
11,700 |
| HFC-125 |
2,800 |
| HFC-134a |
1,300 |
| HFC-143a |
3,800 |
| HFC-152a |
140 |
| HFC-227ea |
2,900 |
| HFC-236fa |
6,300 |
| HFC-4310mee |
1,300 |
| CF4 |
6,500 |
| C2F6 |
9,200 |
| C4F10 |
7,000 |
| C6F14 |
7,400 |
| SF6 |
23,900 | .gif) Source: (IPCC 1996). Source: (IPCC 1996).
.gif) * The methane GWP includes the direct effects and
those indirect effects due to the production of tropospheric ozone
and stratospheric water vapor. The indirect effect due to the
production of CO2 is not included. * The methane GWP includes the direct effects and
those indirect effects due to the production of tropospheric ozone
and stratospheric water vapor. The indirect effect due to the
production of CO2 is not included.

Next
Section ...
|
Home || Emissions
|| National
Site Map || Glossary || Search || Comments || US EPA

http://www.epa.gov/globalwarming/emissions/national/gwp.html
Last
Updated on April 6,
2001
|