Diatomic Ideal Gas
Prerequisites
Before approaching this topic, students should:
- Know the first and second laws of thermodynamics.
- Have familiarity with quantum operators and the energy eigenvalue equation.
- Be proficient in summation notation and performing integrals.
- Know how to utilize limiting cases to make problems solvable.
In-class Content
Lecture: Reviewing Several Energy Eigenvalues (10 minutes)
- Review the different eigenvalues covered in the previous quantum paradigms
- Particle in a box
- Harmonic oscillator
- Rotating molecules
Lecture notes from Dr. Roundy's 2014 course website:
I'm going to quickly review and introduce the energy eigenvalues for some simple quantum mechanical problems. For each of the following, I will sketch out the potential, then sketch the wavefunctions and the spacing of the energy levels.
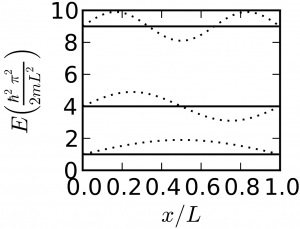
The first problem you handled was a particle in an infinite square well potential: $$\mathcal{H} = \frac{-\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}$$ $$E_n = \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 n^2}{2m L^2}$$ where $n≥1$. We could solve the same problem in three dimensions, and the three coordinates would separate (i.e. we could use separation of variables), and we would have: $$\mathcal{H} = \frac{-\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2$$ $$= -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} - \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2} - \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial z^2}$$ $$ E_{n_xn_yn_z} = \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{L^2}$$
Rigid rotor
The next moderately simple problem is the rigid rotator. In this case, the only energy in the Hamiltonian is the angular kinetic energy: $$\mathcal{H} = \frac{-\hbar^2}{2I}L^2$$ $$E_{lm} = \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I}$$
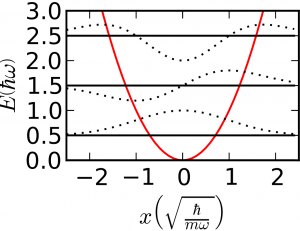
Finally, we have a simple problem that hasn't yet come up in the paradigms, which is the simple harmonic oscillator. In this case we have both kinetic and potential energy: $$\mathcal{H} = \frac{-\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} + \frac{m\omega_0^2}{2}x^2$$ $$E_{n} = \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0$$ Of course, you also studied the hydrogen atom, but its solution is less general than those we've listed here. Any diatomic molecule behaves like a rigid rotator and a simple harmonic oscillator, and like a particle in a box, too!
Lecture on Finding the Internal Energy of a Diatomic Ideal Gas (20 minutes)
- This lecture should immediately follow a review of energy eigenstates and eigenvalues
 (add a link to lecture)
(add a link to lecture)
- Move on to discuss the eigenstates of a Diatomic Ideal Gas, and where they come from.
- Show a calculation of the internal energy. This is a lengthy calculation, so be sure to stop along the way and ask students if they are able to follow. This is an excellent time to stop for a SWBQ
 (add a link to SWBQ main page), to see if students are able to get the next step of the equation.
(add a link to SWBQ main page), to see if students are able to get the next step of the equation.
Lecture notes from Dr. Roundy's 2014 course website:
Let's consider a diatomic ideal gas, such as nitrogen. In this case, the energy levels of a single molecule are given by the sum of the translational kinetic energy, rotational kinetic energy and vibrational energy—both kinetic and potential: $$E_{n_xn_yn_zn_vlm}^{(1)} = \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2} + \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I} + \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0$$ That's an awful lot of quantum numbers, and that's just one molecule, and we're neglecting any possible electronic excited states, anharmonicity or coupling of rotation with vibration!
How does this change when we've got $N$ molecules all confined in the same box? We've already talked about how energies relate when we combine systems: $$E_\text{tot} = \sum_i^N E_i^{(1)}$$ where I've left out all the quantum numbers, since there are so very many.
If we want to know the internal energy, we'll need to sum over every possible state, with the probability of that particular state. To do this, we'll need to know the partition function, so let's start with that. $$Z = \sum^\text{all states} e^{-\beta E_\text{this state}}$$ $$= \sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} e^{-\beta \left(E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)} + E_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}^{(2)} + \cdots\right)}$$ … except that this isn't quite right. We can't distinguish between the different molecules… when we swap two of them in the sum, we're really talking about the same state! We can fix this double-counting by multiplying by an $N!$, which gives us: $$Z = \frac{1}{N!}\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} e^{-\beta \left(E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)} + E_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}^{(2)} + \cdots\right)}$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!}\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} e^{-\beta E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)}} e^{-\beta E_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}^{(2)}} \cdots$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}e^{-\beta E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)}}\right) \left(\sum_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}e^{-\beta E_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}^{(2)}}\right) \cdots$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm}e^{-\beta E_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm}^{(1)}}\right)^N$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm}e^{-\beta \left( \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2} + \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I} + \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0 \right)}\right)^N$$ $$\frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm}e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2}} e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I}} e^{-\beta \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0}\right)^N $$ $$\frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}}e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2}} \sum_{n_{v}}e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I}} \sum_{lm}e^{-\beta \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0}\right)^N$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!} \left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}}e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2}}\right)^N \left(\sum_{n_{v}}e^{-\beta \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I}}\right)^N \left(\sum_{lm}e^{-\beta \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0}\right)^N$$ Now, if we were computing the internal energy $U$, we'd be able to do something very similar: $$= \sum_i P_i E_i$$ $$= \frac{1}{N!}\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} P_{…} E_\text{tot} $$ $$= \frac{1}{N!}\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} P_{…} \left(E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)} + E_{n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2}^{(2)} + \cdots\right) $$ $$= \frac{N}{N!}\sum_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1, n_{x_2}n_{y_2}n_{z_2}n_{v_2}l_2m_2,\cdots} P_{…} E_{n_{x_1}n_{y_1}n_{z_1}n_{v_1}l_1m_1}^{(1)}$$ $$= N\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm} P_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm} E_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm}^{(1)}$$ $$= N\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm} P_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}n_{v}lm} \left( \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2} + \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I} + \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0 \right) $$ $$= N\left(\sum_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}} P_{n_{x}n_{y}n_{z}} \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2 \left(n_x^2 + n_y^2 + n_z^2\right)}{2mL^2} + \sum_{lm} P_{lm} \frac{\hbar^2 l(l+1)}{2I} + \sum_{n_{v}} P_{n_{v}} \left(n + \frac12\right)\hbar \omega_0 \right)$$ So you can see, if we can work out the average translational kinetic energy, rotational energy and vibrational energy of a molecule in this gas, then we'll easily have the total internal energy of this system just by adding everything up and multiplying by $N$.
Diatomic molecule from quantum up
I'm going to divide you into groups. Each group will have a separate task, so that hopefully when we're done as a class we'll have an answer for the total internal energy of a diatomic ideal gas.
These sums are pretty challenging, so I'll ask each group to consider one of two distinct limits: the low-temperature limit and the high-temperature limit. The low- and high-temperature limits have a different meaning for each term in the energy.
For the translational kinetic energy, the limits will be defined by $$\beta \frac{\hbar^2\pi^2}{2mL^2} \gg 1$$ or the reverse. For the rotational energy, it will be $$\beta \frac{\hbar^2}{2I} \gg 1$$ and for the vibrational energy, it will be $$\beta \hbar \omega_0 \gg 1$$ These energy scales have large gaps, so the translational energy may be in the high-temperature limit while the other two are in the low-temperature limit, for instance.
I'd like each group to do one term in the energy, in either the low-temperature limit or the high-temperature limit, but let's not do the low-temperature limit of the translational kinetic energy. The reason we avoid that particular limit is that we've ignored the possibility that two of our molecules may be in precisely the same state. You know the Pauli exclusion principle for electrons (and fermions in general), which means we could have a problem. For bosons (all particles that aren't fermions) there is another problem, which I also won't go into. As long as our temperature is high enough that the probability of any given state is pretty low, we won't run into these troubles (which could give us things like a Bose-Einstein condensate).
Activity: Calculating the Internal Energy of a Diatomic Ideal Gas
Link to Calculating the Internal Energy of a Diatomic Ideal Gas Activity
Activity Highlights
- This small group activity is designed to help students understand how statistical mechanics is applied to concrete systems.
- Students use the vibrational, rotational, and translational energy levels of an ideal diatomic gas to predict the dependence of internal energy on temperature at either high or low temperature.
- The compare-and-contrast wrap-up addresses the process of taking low and high temperature limits, and introduces the equipartition theorem.