Chemistry 122 Winter 2000 Oregon State University
Final Exam March 16, 2000 Dr. Richard Nafshun
DO NOT OPEN THIS EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED.
CALCULATORS ARE NOT TO BE SHARED.
Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" notecard, and your University ID Card. You may use a TI-25X Solar calculator if you wish. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT. Or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room.
Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your last name, first name, middle initial, and student identification number. Leave the class section number and the test form number blank.
1. There are ___ unpaired electrons in a ground-state fluoride ion.
(a) 0.
(b) 1.
(c) 2.
(d) 7.
(e) 15.
2. The ground-state electron configuration of a magnesium ion is:
(a) 1s22s23s23p1.
(b) 1s22s23s1.
(c) 1s22s22p1.
(d) 1s22s22p6.
(e) 1s22s22p3.
3. A ground-state phosphorous atom has:
(a) 1 valence electron.
(b) 2 valence electrons.
(c) 3 valence electrons.
(d) 5 valence electrons.
(e) 7 valence electrons.
4. There is/are ___ lone pair(s) of electrons on the carbon atom in carbon dioxide.
(a) 0.
(b) 1.
(c) 2.
(d) 3.
(e) 4.
5. I2 has been isolated and characterized. The Lewis Symbol for I2 indicates the
iodine-iodine bond is a:
(a) single bond.
(b) double bond.
(c) triple bond.
(d) quadruple bond.
6. The Cl-C-Cl bond angle in tetrachloromethane (CCl4) is:
(a) 90°.
(b) 120°.
(c) 109.5°.
(d) Greater than 109.5°.
(e) Less than 109.5°.
7. The H-N-H bond angle in NH3 is:
(a) 90°.
(b) 120°.
(c) 109.5°.
(d) Greater than 109.5°.
(e) Less than 109.5°.
8. The O-N-O bond angle in the nitrate anion (NO3-) is:
(a) 90°.
(b) 120°.
(c) 109.5°.
(d) Greater than 109.5°.
(e) Less than 109.5°.
9. The oxygen-oxygen bond order in the ozone molecule (O3) is:
(a) 1.00.
(b) 1.33.
(c) 1.50.
(d) 2.00.
(e) 3.00.
10. Consider CH4, CF4, CHF3, H2, and F2. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) CH4 is a polar molecule.
(b) CF4 is a polar molecule.
(c) CHF3 is a polar molecule.
(d) The fluorine-fluorine bond in F2 is polar covalent.
(e) CH4, CF4, CHF3, H2, and F2 are all nonpolar.
11.
Consider the molecule below. The
hybridization of the carbon atom on the right is: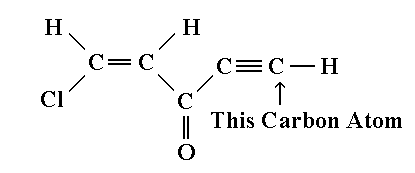
(a) s.
(b) sp.
(c) sp2.
(d) sp3.
(e) sp4.
12. Consider CH3CClCClCH3, CF3CH2CH2CF3, CH3CHC(CCl3)2, and CH3CHCCl2. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) CH3CClCClCH3 can exist as cis-trans isomers.
(b) CF3CH2CH2CF3 can exist as cis-trans isomers.
(c) CH3CHC(CCl3)2 can exist as cis-trans isomers.
(d) CH3CHCCl2 can exist as cis-trans isomers.
(e) CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3CHCHCH3, CH3CHC(CH3)2, and CH3CHCCl2 can all exist as
cis-trans isomers.
13. Consider sodium chloride, calcium chloride, aluminum oxide, aluminum chloride, and aluminum fluoride. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Sodium chloride has the highest melting point.
(b) Calcium chloride has the highest melting point.
(c) Aluminum oxide has the highest melting point.
(d) Aluminum chloride has the highest melting point.
(e) Aluminum fluoride has the highest melting point.
14. The formal charge on the central atom in ozone is:
(a) 0.
(b) -1.
(c) +1.
(d) -2.
(e) +2.
15. Consider CHCH. The molecule contains:
(a) no p-bonds.
(b) one p-bond.
(c) two p-bonds.
(d) three p-bonds.
16. Molecular orbital theory predicts the F22- ion is:
(a) diamagnetic.
(b) paramagnetic.
(c) ferromagnetic.
(d) fluoromagnetic.
(e) neomagnetic.
17. The molecular shape of BeH2 is:
(a) linear.
(b) bent.
(c) trigonal planar.
(d) tetrahedral.
(e) octahedral.
18. Consider CH3OCH3, H2, H2O, O2, and F2. The molecule with the highest boiling point is:
(a) CH3OCH3.
(b) H2.
(c) H2O.
(d) O2.
(e) F2.
19. A student places 120.00 grams of calcium chloride into 2000.00 grams of water. The boiling point of this solution is:
(a) °C.
(b) °C.
(c) °C.
(d) °C.
(e) °C.
20. Consider the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide:
H2O2 ---> O2 + H2
O2 is found to be forming at a rate of 1.00 Ms-1, at what rate is H2O2 disappearing?
(a) 1.00 Ms-1
(b) 0.50 Ms-1
(c) 0.25 Ms-1
(d) 2.00 Ms-1
(e) 4.00 Ms-1
21.
Given the following kinetic data for the reaction A + 2B ® C
Experiment |
Initial [A], M |
Initial [B], M |
Initial Rate, Ms-1 |
1 |
0.100 |
0.100 |
0.0025 |
2 |
0.100 |
0.200 |
0.0100 |
3 |
0.200 |
0.100 |
0.0100 |
The rate law for the reaction is:
(a) Rate = k [A][B].
(b) Rate = k [A][B]2.
(c) Rate = k [A]2[B].
(d) Rate = k [A]0[B]2.
(e) Rate = k [A]2[B]2.
YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT
22. A student places 125.0 mg of an unknown protein into 15.00 mL of water and measures the
osmotic pressure to be 7.50 torr at 125.00 °C. Determine the molar mass of the protein.
[R = 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K]
23. The decomposition of H2O2 follows first order kinetics (i.e. Rate = k [H2O2]). Given that the initial concentration of H2O2 was 1.382 M and its concentration after 22.0 s was 0.445 M what is the rate constant (k) for the reaction? What concentration remains after 75.0 s?
24. Sketch the pH scale and label the acidic and basic regions.
25. Calculate the pH of a 0.405 M aqueous benzoic acid.
26. Consider 0.500 M HCOOH (aq) and 0.500 M CH3COOH (aq). Without doing a calculation, determine which has a lower pH. Explain.
27. Write the equilibrium expression for the combustion of methane gas.
28. A student measures the pH of a solution to be 2.75. Calculate [H3O+]. Is this solution acidic?
29. A student measures the pH of a solution to be 7.01. Calculate [H3O+]. Is this solution acidic?
30. Calculate the pH of 0.056 M HCl (aq). Is this solution acidic?
31. Consider 0.2500 M HCl (aq) and 0.2500 M CH3COOH (aq). Without doing a calculation, determine which has a lower pH. Explain.
32. Consider 0.1200 M HCl (aq) and 0.1200 M HNO3 (aq). Without doing a calculation, discuss the relative pH values.
10. Consider 0.200 M HCl (aq) and 0.4100 M HCl (aq). Without doing a calculation, discuss the relative pH values.
11. Without doing a calculation discuss the relative values of [H3O+] and [OH-] in 0.200 M HCl (aq).