 (where R = 8.314 kg•m2/s2•mol•K, and
molar mass is in kg/mol)
(where R = 8.314 kg•m2/s2•mol•K, and
molar mass is in kg/mol)Chemistry 121 Fall 2003 Oregon State University
Exam 2 November 20, 2003 Dr. Jennifer Travers
Dr. Richard Nafshun
DO NOT OPEN THIS EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED.
CALCULATORS ARE NOT TO BE SHARED.
Instructions: You should have with you several number two pencils, an eraser, your 3" x 5" notecard, and your University ID Card. You may use a basic calculator (for example, TI-25X Solar or TI-30XA) if you wish. If you have notes or electronic devices with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT.
Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your last name, first name, middle initial, and student identification number. Leave the class section number blank. Enter the following test form number:
This exam consists of 25 multiple-choice questions worth four points each Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the scantron. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions during the exam, please raise your hand to attract the attention of a proctor. The proctor will come to you. Present your ID card when submitting the exam. You may keep the multi-choice portion of this exam, so please mark the answers you selected on it.
Equations or constants you might need:
R = 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K R = 8.314 J/mol K PV = nRT P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
K = 273.15 + °C 760 Torr = 1 atm = 760 mm Hg Avogadro’s Number = 6.02 x 1023
mrms = (where R = 8.314 kg•m2/s2•mol•K, and
molar mass is in kg/mol)
(where R = 8.314 kg•m2/s2•mol•K, and
molar mass is in kg/mol)
1. How much 0.810 M H2SO4 solution is needed to prepare 1.00 L of
0.331 M H2SO4?
(A) 409 mL
(B) 491 mL
(C) 268 mL
(D) 2.45 mL
2. A student dissolves three moles of MgCl2 into a beaker. How many chloride ions are present in the solution?
(A) There are 3.61x 1024 chloride ions in the beaker.
(B) There are 1.81 x 1024 chloride ions in the beaker.
(C) There are 5.73 x 1025 chloride ions in the beaker.
(D) There are 3.60 x 1025 chloride ions in the beaker.
(E) There are 1.08 x 1026 chloride ions in the beaker.
3. Which is the strongest electrolyte when dissolved in water?
(A) an ice cube
(B) hydrochloric acid
(C) methane
(D) ammonia
(E) acetic acid
4. Which of the following lists contains only acids?
(A) HNO3, NaNO3, HCl
(B) HNO3,CH3CO2H, H2SO4
(C) NaOH, KOH, NH4OH
(D) NH3, H2SO4, HCl
5. A student mixes an aqueous solution of sodium phosphate with an aqueous solution of calcium nitrate, and a precipitate forms. The precipitate is:
(A) Ca3(PO4)2(s)
(B) Na3PO4(s)
(C) Ca(NO3)2(s)
(D) NaNO3(s)
(E) Na2O
6. Aqueous solutions of chromium(III) bromide and lithium hydroxide are mixed, and a single precipitate forms. Complete the following reaction and give the net ionic equation:
Cr3+(aq) + 3 Br-(aq) + Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) à
(A) Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) à LiOH(s)
(B) 3 Li+(aq) +3 Br- (aq)à 3 LiBr(s)
(C) Cr3+ (aq) + 3 Br- (aq)à CrBr3(s)
(D) Cr3+ (aq)+ 3 OH- (aq) à Cr(OH)3(s)
7. Five molecules of hydrochloric acid are dissolved in pure water and titrated with sodium hydroxide. What point in the titration does the beaker below represent?
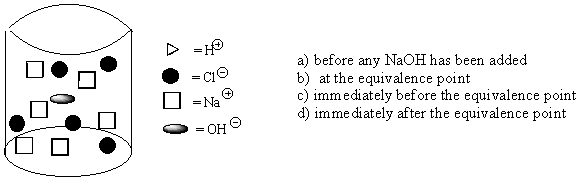
8. Which of the following statements about gases is not true?
(A) Gas molecules move faster than liquid molecules.
(B) There are strong attractions between ideal gas molecules.
(C) Collisions of gas molecules are random.
(D) The total energy of gas molecules are not changed by collisions.
9. A student obtains 25.00 mL of an HCl solution of unknown concentration. Upon
titration, 30.64 mL of 0.09230 M NaOH are required for neutralization.
Determine the concentration of the HCl solution.
(A) 0.1131 M.
(B) 0.07445 M.
(C) 0.07120 M.
(D) 0.8840 M.
(E) 8.840 M.
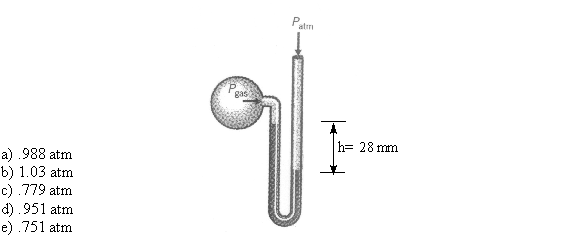
10. You use an open ended mercury manometer in your laboratory to measure the gas shown below. If the atmospheric pressure in your laboratory is 751 mm Hg, what is the pressure of the gas in the flask?
11. A balloon initially filled to 1.0 L has a pressure of 1.34 atm. A pretty lady daintily
reduces the volume until the pressure is 1.67 atm. What is the final volume of the
balloon?
(A) 0.340 L
(B) 1.25 L
(C) 0.802 L
(D) 2.24 L
(E) 3.01 L
12. If a fixed amount of gas occupies 2.53 m3 at a temperature of -15°C and 191 torr, what volume will it occupy at 25° C and 672 torr?
(A) 0.623 m3
(B) 0.489 m3
(C) 2.92 m3
(D) 0.831 m3
13. Consider a fixed amount of gas. Which of the following is FALSE?
(A) When the temperature is increased at constant volume, the pressure increases.
(B) When the volume is increased at constant temperature, the pressure increases.
(C) When the temperature is decreased at constant pressure, the volume decreases.
(D) When the pressure is increased at constant temperature, the volume decreases.
14. What is the temperature of a sample of 23.2 g of CO2 that occupies 0.864 L at
0.765 atm?
(A) 65.4 K
(B) 0.35 K
(C) 15.3 K
(D) 568 K
15. What is the molar mass of a gas if .551 g occupies 179mL at 751 mm Hg and
359 K?
(A) 167 g/mol
(B) 39.9 g/mol
(C) 91.8 g/mol
(D) 22.0 g/mol
16. A mixture of gases contains 2.3 mole of CO2, 0.51 mole of O2, and 0.74 mole of
N2. The mixture has a total pressure of 745 torr. What is the partial pressure from the O2?
(A) 143 torr
(B) 842 torr
(C) 379 torr
(D) 107 torr
17. When the following reaction is carried out in a flask, the flask feels COLD when
held in the hands:
NH4NO3 (s) + (H2O) ® NH4+ (aq) + NO3- (aq)
Which of the following is TRUE?
(A) Heat is transferred from the hand to the flask; this is an endothermic process.
(B) Heat is transferred from the flask to the hand; this is an endothermic process.
(C) Heat is transferred from the flask to the hand; this is an exothermic process.
(D) Heat is transferred from the hand to the flask; this is an exothermic process.
18. The chemical process XàY gives off 382 J of heat to the surroundings, and does 28 J of work on the surroundings. What is the change in internal energy (ΔE) for the system?
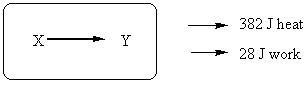
(A) + 354 J
(B) – 354 J
(C) – 410 J
(D) + 410 J
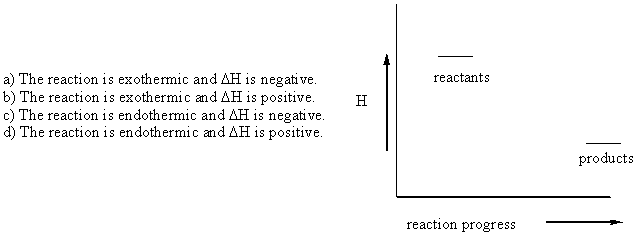
19. Which of the following statements best describes the enthalpy diagram shown:
20. A sample of radiator coolant requires 932 J to raise the temperature from -5°C to
132°C. What is the heat capacity of the coolant?
(A) 6.80 J/°C
(B) 35.3 J/°C
(C) 6.34 J/°C
(D) 186.4 J/°C
21. Which of the following equations is endothermic?
(A) CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) à CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
(B) H2O(g) à H2O(l)
(C) CO2(g) à CO2(s)
(D) H2O(s) à H2O(l)
(E) N2(g) à N2(l)
22. Consider the reaction of hydrogen gas with chlorine gas to make hydrochloric acid.
H2(g) + Cl2 (g) à 2 HCl(g) DH= -184.6 J
What is the enthalpy change when 15.8 g of H2(g) reacts with excess Cl2(g)?
(A) –81.0 J
(B) -2.92 kJ
(C) –1.46 kJ
(D) –11.64 J
23. Use the data in the table below to answer the following question:
DH°f (kJ/mol)
CO2 (g) −393.5
C6H6 (g) + 49.0
H2O (l) −285.9
What is ΔH˚reaction for the following reaction?
C6H6 (l) + 15/2 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l)
(A) -335 kJ.
(B) +335 kJ.
(C) -3268 kJ.
(D) -6535 kJ.
(E) -8368 kJ.
24. The heat of formation (DH°f) of NH4Cl (s) is –315.4 kJ/mol. The chemical equation associated with this reaction is:
(A) ½ N2 (g) + 4 HCl (aq) → NH4Cl (s) + 3/2 Cl2 (g)
(B) ½ N2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) + ½ Cl2 (g) → NH4Cl (s)
(C) NH4+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → NH4Cl (s)
(D) NH4+ (s) + Cl- (s) → NH4Cl (s)
(E) NH4 (s) + Cl (g) → NH4Cl (s)
25. Determine DH° for this reaction:
2 N2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 2 N2O5(g)
using the following three equations:
|
H2(g) + (1/2) O2(g) → H2O(l) |
DH° = -285.8 kJ |
|
N2O5(g) + H2O(l) → 2HNO3(l) |
DH° = -76.6 kJ |
|
2 N2(g) + 6 O2(g) + 2 H2(g) → 4 HNO3(l) |
DH° = -696.4 kJ |
(A) -95.8 kJ.
(B) + 371 kJ.
(C) +28.4 kJ.
(D) -1059 kJ.
(E) +1345 kJ.